Abstract
INTRODUCTION: C-C chemokine receptor-like 2 (CCRL2) is an atypical chemokine receptor normally expressed in differentiated myelocytes that activates inflammatory signaling1. We showed that CCRL2 is upregulated in CD34+ cells from myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients and CD34+ blasts from patients with secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) compared to cells from healthy individuals and patients with de novo AML2. CCRL2 upregulates IL-3-mediated JAK2/STAT signaling in MDS cells2. JAK2/STAT pathway is critical for the growth of leukemias with erythroid and megakaryocytic (EM) differentiation3. The aim of this study was to study CCRL2 expression in AML cells with EM differentiation and describe the effect of CCRL2 deletion by CRISPR-Cas9 in the growth of cytokine-dependent erythroleukemia cells in vitro and in vivo.
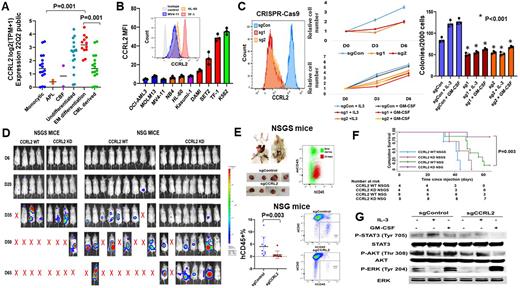
METHODS: CCRL2 RNA levels from 54 AML cell lines available in DepMap portal were analyzed. Various AML cell lines were stained for CCRL2 and analyzed by flow cytometry. TF-1 cells were transduced with two sgCCRL2/Cas9 expressing lentiviruses with sg-Scramble RNA as control and selected with puromycin. Cell counting and methylcellulose-based assays were used to assess the impact of CCRL2 deletion in vitro. CCRL2 wild-type (WT) and knockdown (KD) TF-1 cells were transduced with GFP/Luciferase dual-reporter retroviruses and injected in NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Wjl Tg(CMV-IL3,CSF2,KITLG)1Eav/MloySzJ (NSGS) mice, which secrete human IL-3, GM-CSF and c-Kit, and in NOD.Cg-Prkdcscid Il2rgtm1Wjl/SzJ (NSG) mice, which do not secrete these cytokines (106/mice) 48 hours after Chlophosome-A chlodronate liposome injection. IVIS bioluminescence imaging was used to monitor TF-1 growth. Survived mice were sacrificed at day 65 and percentage of human cells in marrow, spleen and extra-medullary masses was measured by human CD45. Kaplan-Meier was used to assess survival differences. STAT3/AKT/ERK phosphorylation was measured after cytokine deprivation for 48 hours followed by treatment with IL-3 (20 ng/ml) or GM-CSF (6 ng/ml) for 30 minutes by western blot (WB).
RESULTS: AML cells with EM differentiation have the highest CCRL2 RNA levels (Fig. 1A). Erythroleukemia cell lines (DAMI, SET2, TF-1) express higher CCRL2 compared to cell lines with monocytic differentiation, APL cell lines and Kasumi-1 (core-binding factor) (Fig. 1B). To study the role of CCRL2 in cytokine-regulated growth of erythroleukemia cells, we focused on the cytokine-dependent TF-1 cells. CCRL2 deletion by two sgRNAs (sg1 and sg2) suppresses their growth and clonogenicity both in the presence and absence of IL-3 (10 ng/ml) and GM-CSF (2 ng/ml) (Fig. 1C). TF-1 cells engraftment in NSGS mice led to extra-medullary masses of leukemia cells without bone marrow involvement (Fig. 1D). CCRL2 deletion only mildly affected the growth of TF-1 cells in NSGS mice (Fig. 1D, E) and did not lead to significant survival prolongation (Fig. 1F). The engraftment of TF-1 cells in NSG mice led to a milder phenotype with bone marrow involvement only (Fig. 1D), which was significantly suppressed by CCRL2 deletion (Fig. 1D, E). NSG mice injected with CCRL2 KD cells had significantly prolonged survival (Fig. 1F). CCRL2 deletion suppresses STAT3, AKT and ERK phosphorylation in TF-1 cells under cytokine deprivation and decreases the IL-3-mediated STAT3 phosphorylation (Fig. 1F). However, CCRL2 KD TF-1 cells show more prominent GM-CSF-mediated ERK phosphorylation compared to WT cells.
CONCLUSIONS: AML cell lines with EM differentiation express higher CCRL2 compared to other AML cell lines. CCRL2 deletion by CRISPR-Cas9 suppresses TF-1 growth in vitro and in vivo especially in the absence of cytokines. CCRL2 may be implicated in the activation of STAT, AKT and ERK pathways in the absence of cytokines but GM-CSF-mediated ERK upregulation could be a mechanism of rescue of TF-1 cells from CCRL2 deletion.
REFERENCES 1. Del Prete A, Martínez-Muñoz L, Mazzon C, et al. The atypical receptor CCRL2 is required for CXCR2-dependent neutrophil recruitment and tissue damage. Blood. 2017;130(10):1223-1234.
2. Karantanos T, Teodorescu P, Perkins B, et al. The role of the atypical chemokine receptor CCRL2 in myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Sci Adv. 2022;8(7):eabl8952.
3. Fagnan A, Piqué-Borràs MR, Tauchmann S, Mercher T, Schwaller J. Molecular Landscapes and Models of Acute Erythroleukemia. Hemasphere. 2021;5(5):e558.
Disclosures
Ghiaur:Menarini Group: Consultancy, Research Funding; Syros Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Scripps: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.